문제 설명
초 단위로 기록된 주식가격이 담긴 배열 prices가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 가격이 떨어지지 않은 기간은 몇 초인지를 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성하세요.
제한사항- prices의 각 가격은 1 이상 10,000 이하인 자연수입니다.
- prices의 길이는 2 이상 100,000 이하입니다.
| [1, 2, 3, 2, 3] | [4, 3, 1, 1, 0] |
- 1초 시점의 ₩1은 끝까지 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
- 2초 시점의 ₩2은 끝까지 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
- 3초 시점의 ₩3은 1초뒤에 가격이 떨어집니다. 따라서 1초간 가격이 떨어지지 않은 것으로 봅니다.
- 4초 시점의 ₩2은 1초간 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
- 5초 시점의 ₩3은 0초간 가격이 떨어지지 않았습니다.
문제를 보면서
자신보다 뒤에 있는 원소들을 비교하고 자신을 지워가면서 가격 비교를 하면 될 것같다는 생각이 들었다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
int[] answer = new int[prices.Length];
int sec=0;
Queue<int> queue= new Queue<int>(prices);
int now=queue.Dequeue();
for(int i=0;i<queue.Count;i++)
{
//떨어졌다면
if(now>queue.ElementAt(i))
{
sec++;
//if(queue.Count==0) sec=0;
answer[i]=sec;
}
//떨어지지 않음, 증가 또는 동일
else
{
sec++;
}
}
return answer;
}
}


4는 끝까지 떨어지지 않기때문에 answer 배열에 아무것도 추가되지 않았던것임
--> 떨어지지 않는 경우에도 조건문을 추가해야함
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
int[] answer = new int[prices.Length];
int sec=0;
int now_index=0;
Queue<int> queue= new Queue<int>(prices);
while(now_index<prices.Length){
int now=queue.Dequeue();
for(int i=0;i<queue.Count;i++)
{
//떨어졌다면
if(now>queue.ElementAt(i))
{
sec++;
answer[i]=sec;
}
//떨어지지 않음, 증가 또는 동일
else
{
sec++;
//마지막까지 다 돌았다면 answer배열에 값 추가 조건문
if(i==queue.Count-1)
{
answer[now_index]=sec;
}
}
}
now_index++;
sec=0;
}
return answer;
}
}
이런식으로 답이랑 전혀 다름
메모장에 내가 짠 코드를 실행과정을 작성해봄 (일단 answer[0] 만 확인,now index=0일때 )

하지만 answer[0] = 4 가 나오도록 작성했는데 왜 1이 나오는것이지??
Console.WriteLine으로 찍어봤다.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
int[] answer = new int[prices.Length];
int sec=0;
int now_index=0;
Queue<int> queue= new Queue<int>(prices);
while(now_index<prices.Length){
int now=queue.Dequeue();
for(int i=0;i<queue.Count;i++)
{
//떨어졌다면
if(now>queue.ElementAt(i))
{
sec++;
Console.WriteLine("값 떨어짐");
//if(queue.Count==0) sec=0;
answer[i]=sec;
}
//떨어지지 않음, 증가 또는 동일
else
{
sec++;
Console.WriteLine("sec: {0}",sec);
//마지막까지 다 돌았다면 answer배열에 값 추가 조건문
if(i==queue.Count-1)
{
answer[now_index]=sec;
Console.WriteLine("now_index: {0}, sec: {1}",now_index,sec);
Console.WriteLine("answer[now_index]: {0}",answer[now_index]);
Console.WriteLine("for문 다 돌았다");
}
}
}
now_index++;
sec=0;
Console.WriteLine("answer[0]: {0}",answer[0]);
}
return answer;
}
}
이것처럼 answer[0]은 4가 잘 저장되어있다가 now_index=2 일때 갑자기 1로 바뀐다?????
아하 코드를 다시 보니
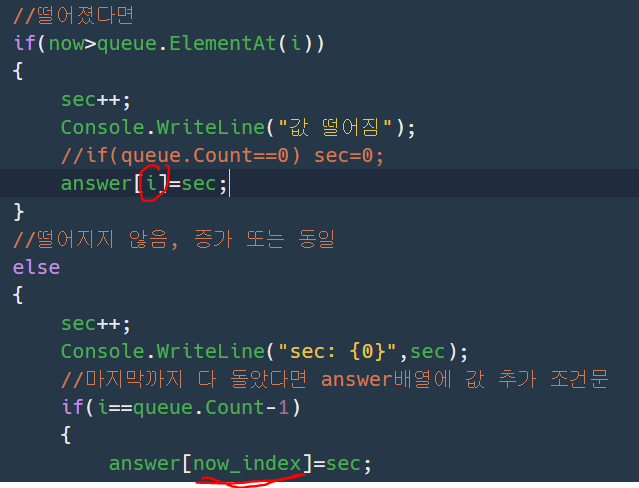
값이 떨어진 경우에서 잘못 작성하였다.
i를 now_index로 수정하자

수정하니 answer[0]의 값은 제대로 변경되었다.
하지만 문제는 answer[2]의 값이 문제다 얘만 답이 다르게 나옴
다시 메모장으로 실행과정 쓰기 ㄱㄱ
작성하면서 문제점을 발견하였다.
가격이 떨어졌다면 바로 값을 리턴하고 for문을 중지해야하는데 즉 break문이 필요 !!
break문이 없어서 계속 for문을 실행하고 sec 값이 증가되고, 마지막까지 돌고나서 다시 값이 새로운 sec값으로 삽입되는 것이 원인
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
int[] answer = new int[prices.Length];
int sec=0;
int now_index=0;
Queue<int> queue= new Queue<int>(prices);
while(now_index<prices.Length){
int now=queue.Dequeue();
for(int i=0;i<queue.Count;i++)
{
//떨어졌다면
if(now>queue.ElementAt(i))
{
sec++;
answer[now_index]=sec;
break;
}
//떨어지지 않음, 증가 또는 동일
else
{
sec++;
//마지막까지 다 돌았다면 answer배열에 값 추가 조건문
if(i==queue.Count-1)
{
answer[now_index]=sec;
}
}
}
now_index++;
sec=0;
}
return answer;
}
}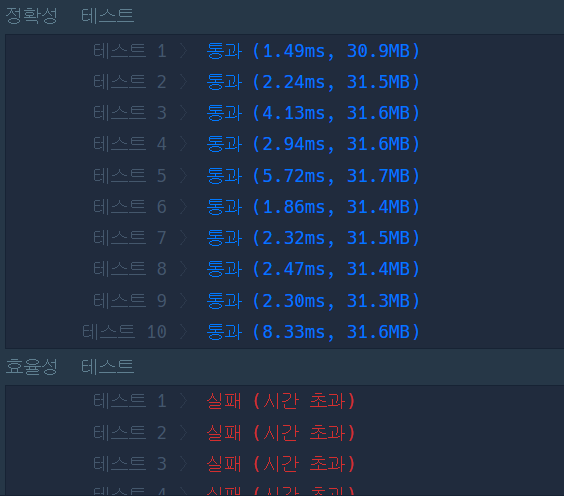
오 근데 효율성 테스트에서 실패했다..
시간복잡도 부분에서 문제인디
chat GPT 한테 물어보쟈 ^0^
각 가격에 대해 큐를 사용하여 내부적으로 반복문을 실행하기 때문에 시간 복잡도가 O(n^2)로 비효율적이기 때문이라고
스택 사용을 권장했다 .
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.Length;
int[] answer = new int[n];
Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 스택이 비어있지 않고 현재 가격이 스택의 최상위 가격보다 낮다면
while (stack.Count > 0 && prices[stack.Peek()] > prices[i]) {
int index = stack.Pop();
answer[index] = i - index; // 가격이 떨어지는 시간을 기록
}
stack.Push(i);
}
// 스택에 남아있는 인덱스는 가격이 끝까지 떨어지지 않은 경우
while (stack.Count > 0) {
int index = stack.Pop();
answer[index] = n - index - 1;
}
return answer;
}
}
queue로 풀이를 하려면
현재 가격이 다음 가격과 비교할 때 떨어지는지 여부만 판단하고, 큐에서 하나씩 빼는 대신 인덱스를 추적하면서 진행하면 된다고 했음
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] prices) {
int[] answer = new int[prices.Length];
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>(prices);
for (int i = 0; i < prices.Length; i++) {
int now = queue.Dequeue();
int sec = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.Length; j++) {
sec++;
if (now > prices[j]) {
break;
}
}
answer[i] = sec;
}
return answer;
}
}하지만 이 풀이도 최악의 경우 시간 복잡도가 O(n^2) 이 될 수 있으므로 스택을 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.
빅오표기법
Big-O(또는 Big-Oh) notation은 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도를 나타내는 표기법이며, O(f(n))으로 나타낸다.
알고리즘의 복잡도를 판단하는 척도로는 시간 복잡도와 공간 복잡도 두 가지가 있는데, 빅오표기법은 시간 복잡도를 다룬다.
O(1)
입력에 관계없이 복잡도는 동일하게 유지
O(N)
입력이 증가하면 처리시간 또는 메모리 사용이 선형적으로 증가한다.
O(n^2)
반복문이 두번있는 경우
O(log n)/ O(nlog n)
입력크기에 따라 처리시간이 증가하는 정렬 알고리즘에서 많이 사용됨
내가 짠 코드는 이중 반복문을 사용하고 있기 때문에 O(n^2) 이다.
재 작성된 코드는 각 주식 가격에 대해 남은 모든 가격을 순회하여 비교하는 방식
스택을 사용하여 한 번의 순회로 해결할 수 있는 방법
하지만 스택을 이용한 풀이도 이중 반복문 아닌가? 라는 의문
스택을 사용하는 알고리즘이 이중 반복문을 사용하는 것처럼 보일 수 있지만, 실제로는 한 번의 순회로 문제를 해결합니다. 이를 이해하기 위해서는 스택을 사용하는 접근 방식의 세부 사항을 살펴보는 것이 중요합니다.
스택을 사용하는 접근 방식에서는 각 요소가 스택에 한 번 추가되고, 한 번 제거됩니다. 따라서, 전체적으로 모든 요소는 최대 두 번 스택과 상호작용합니다. 이를 통해 시간 복잡도를 O(n)으로 유지할 수 있습니다.
'프로그래머스 코딩테스트 연습' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스 코테 C#] Lv1. 평균 구하기 (0) | 2024.09.06 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스 코테 C#] Lv1. 짝수와 홀수 (0) | 2024.08.29 |
| [프로그래머스 코테 C#] Lv2. 프로세스 (0) | 2024.06.14 |
| [프로그래머스 코테 C#] Lv2. 기능개발 (0) | 2024.06.09 |
| [프로그래머스 코테 C#] Lv2. 올바른 괄호 (1) | 2024.06.06 |



